Cardedeu Senior Center
This senior facility seeks for integration in the context, a XIX century textile factory, by re interpreting the traditional industrial brick architecture into industrialized dry assembly fully recyclable terracotta.
This senior citizens centre is the milestone of a public facilities complex that the city of Cardedeu is developing in an old textile factory.
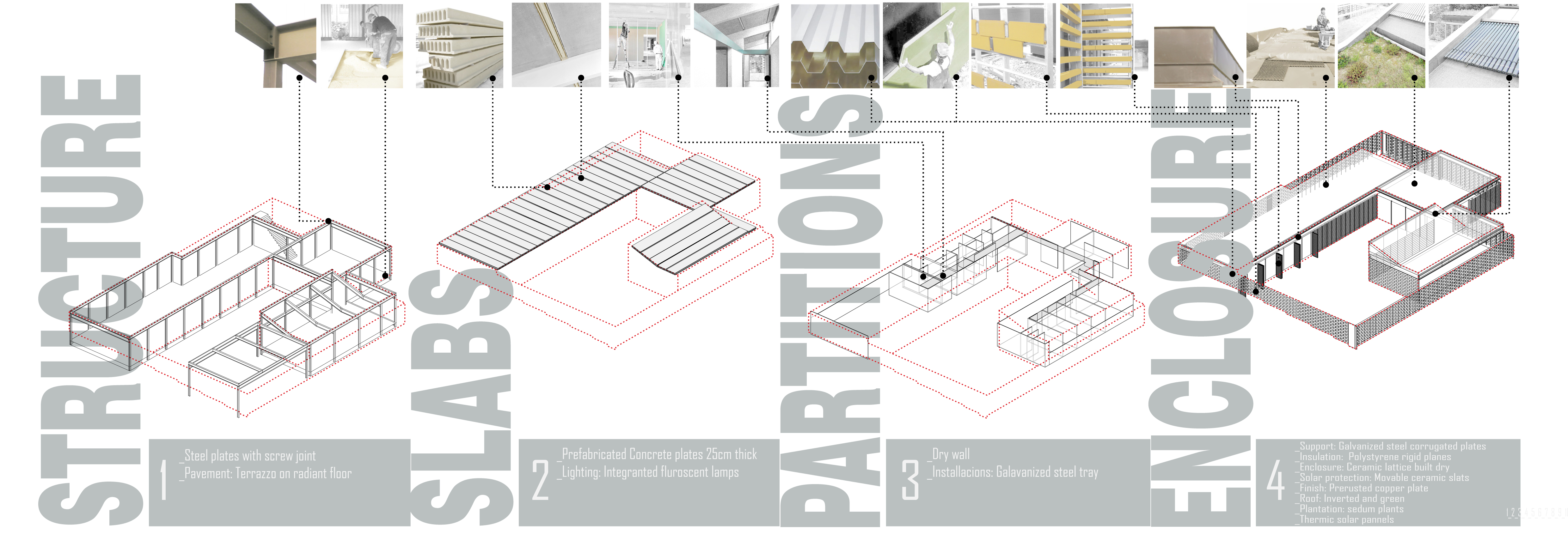
The proposal is based on the redefinition of ready-made components and their assembly to try to optimize the environmental performance of the building as well as the possibility or recycling the used elements. The building was based on dry construction (except the ground) and formally displayed in such a way that increases its capability to interact with the surroundings (both architecturally and environmentally).
We establish the relationship with the context by two decisions:
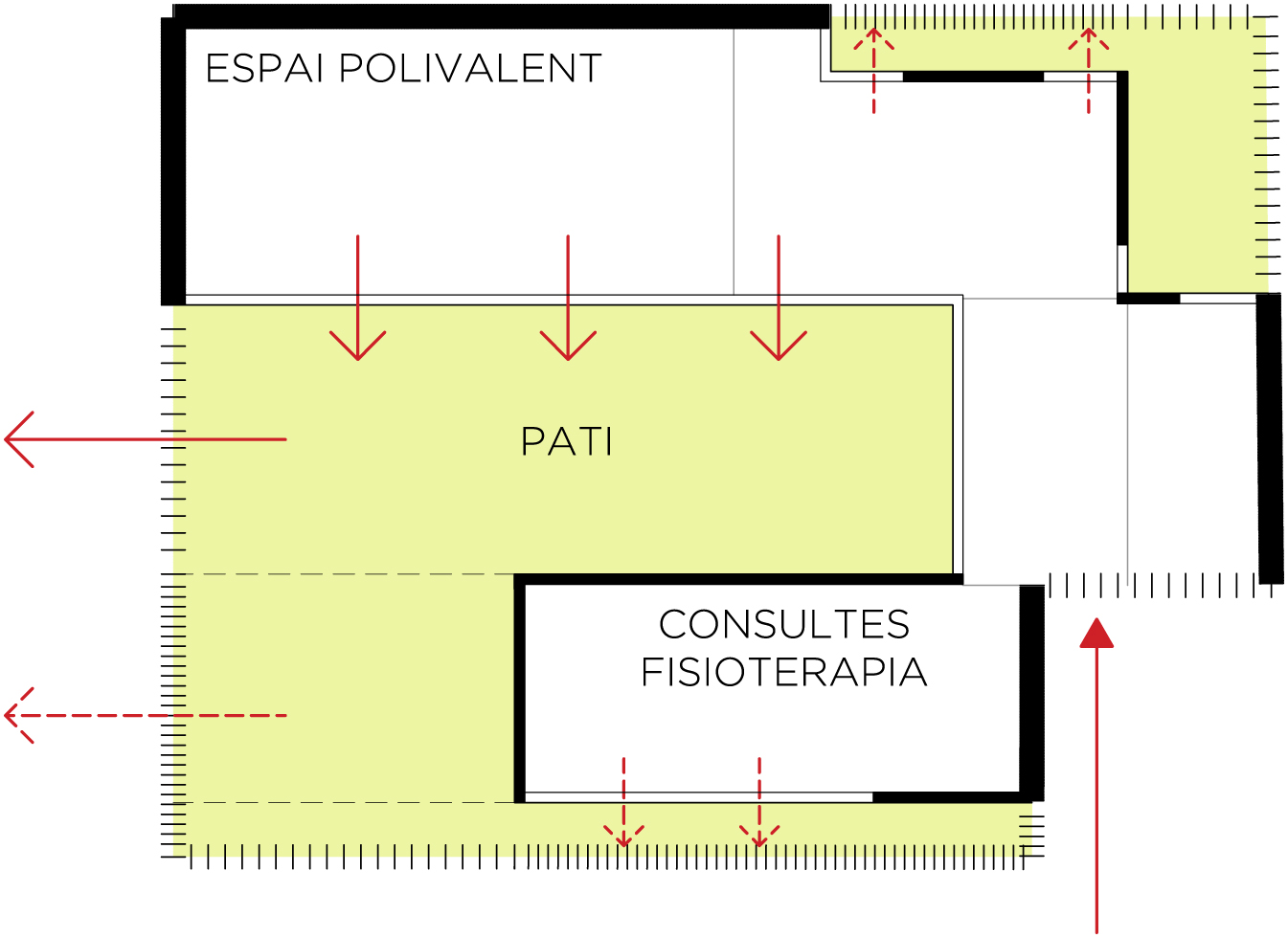
1. The building is organized through a series of three structural bays and orientation similar to the bays of the textile factory, which also serve to build the corner of the block. With a partial and alternate voiding operation on each of the three bays, we generate a series of specialized patios. Patios have different dimensions, proportions and function and relate to different indoor spaces. One open courtyard on the corner of the block organizes access space.
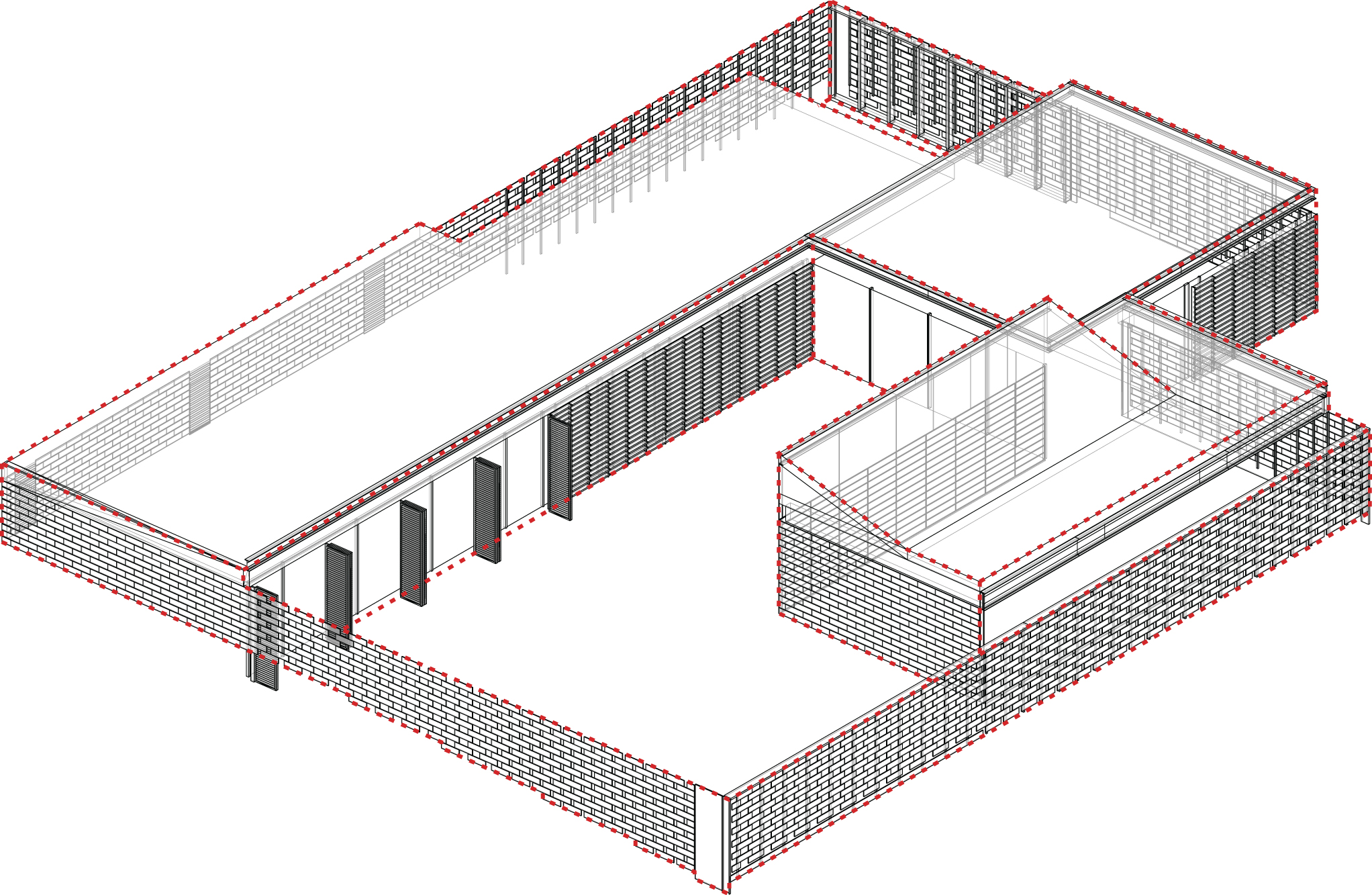
2. Integration of the elderly centre in the textile factory complex is guaranteed by the choice of coating material: entire vertical building envelope is constructed with a single ceramic tile that varies the size of the vertical joint between pieces to generate a palette of walls ranging from blind to very transparent ventilated wall lattices. Depending on the depth of the space behind the wall, from the ventilated façades to intimacy patios and larger yards, a measure of vertical joints between pieces is determined. All transitions from one situation to another are provided by a continuous gradient. Solar, fixed or opening protections against the glass facades, are also made with ceramic slats.
Energy, construction and program sustainability criteria are a key factors in the geometric and material definition of the building and landscape.
Energetic Sustainability
The plan configuration is driven to minimize energy consumption for lighting and climate conditioning. All spaces have a natural ventilation system that uses the patios to cool and humidify the air outside and avoids use of artificial cooling except in extreme heat situations. The green roof and ventilated facade also contribute decisively in order to avoid HVAC use in summer. In winter, the building is heated by a low temperature radiant floor throughout powered by integrated solar panels on the roof. This system is dimensioned so that it is estimated that it will be practically unnecessary to resort to measures of artificial support throughout the year.
Constructive sustainability
Construction system is based on reversibility and materials recycling criteria. We believe that sustainable construction requires reversible constructive processes and must take into account the limited life of the building. Once the building’s lifetime is over, its constituent materials must be reused or recycled. The entire construction, except the floor slab has been carried out dry. The hot rolled steel structure is 100%, so it can be easily dismounted. All other elements are also easily removable and reusable. We have also tried to reduce to minimum the constructive elements. We have avoided suspended ceilings and MEP pipes run along the building in a registrable galvanized plate. This approach has been weighed to the end without harming the performance of the building.
Programmatic sustainability
Flexibility and versatility of use and distribution can extend the useful life of the building. On that purpose, all structural elements have been placed in the perimeter-in order to allow free reconfiguration of the partition walls-and calculated to support a level on top if extension was necessary. All MEP systems have also been designed to allow distribution changes with minor impact on the systems layout.
Cardedeu Senior Center
In collaboration with SiO2arch
Project duration: 2005-2007
Promotor: Ajuntament de Cardedeu
Type: Public Facility
Area: 400 m2
Budget: 0,7 M €
Site: Cardedeu-Barcelona, Spain
Awards: Open Competition, First Prize
Design team: Jordi Ribó
Collaborators: PROISOTEC (MEP), Joan Miquel Riba de Palau (structures) and Mª Teresa Vivó (quantity surveyor)
Constructor: Abelcir
Photography: José Hevia
In collaboration with SiO2arch
Project duration: 2005-2007
Promotor: Ajuntament de Cardedeu
Type: Public Facility
Area: 400 m2
Budget: 0,7 M €
Site: Cardedeu-Barcelona, Spain
Awards: Open Competition, First Prize
Design team: Jordi Ribó
Collaborators: PROISOTEC (MEP), Joan Miquel Riba de Palau (structures) and Mª Teresa Vivó (quantity surveyor)
Constructor: Abelcir
Photography: José Hevia